Doppler radar improves lives by peeking inside air masses to predict the weather. A Purdue University team that includes Dr. John Turek, professor of basic medical sciences, is using similar technology to look inside living cells, introducing a method to detect pathogens and treat infections in ways that scientists never have before.
In a new study, the team used Doppler to sneak a peek inside cells and track their metabolic activity in real time, without having to wait for cultures to grow. Using this ability, the researchers can test microbes found in food, water, and other environments to see if they are pathogens, or help them identify the right medicine to treat antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Dr. David Nolte, Purdue’s Edward M. Purcell Distinguished Professor of Physics and Astronomy; Dr. Eduardo Ximenes, research scientist in the Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering; Dr. Michael Ladisch, Distinguished Professor of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, and Dr. Turek adapted this technique from their previous study on cancer cells in a paper released this month in Communications Biology.
Using funding from the National Science Foundation as well as Purdue’s Discovery Park Big Idea Challenge, the team worked with immortalized cell lines — cells that will live forever unless you kill them. They exposed the cells to different known pathogens, in this case salmonella and E. coli. They then used the Doppler effect to spy out how the cells reacted. These living cells are called “sentinels,” and observing their reactions is called a “biodynamic assay.”
“First we did biodynamic imaging applied to cancer, and now we’re applying it to other kinds of cells,” Dr. Nolte said. “This research is unique. No one else is doing anything like it. That’s why it’s so intriguing.”
This strategy is broadly applicable when scientists have isolated an unknown microbe and want to know if it is pathogenic — harmful to living tissues — or not. Such cells may show up in the food supply, water sources or even in recently melted glaciers.
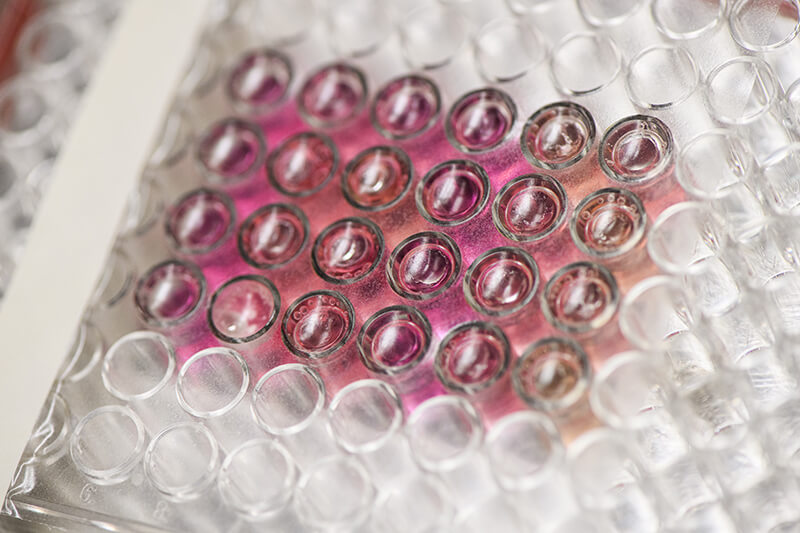

“This directly measures whether a cell is pathogenic,” Dr. Ladisch said. “If the cells are not pathogenic, the Doppler signal doesn’t change. If they are, the Doppler signal changes quite significantly. Then you can use other methods to identify what the pathogen is. This is a quick way to tell friend from foe.”
Being able to quickly discern whether a cell is harmful is incredibly helpful in situations where people encounter a living unknown microorganism, allowing scientists to know what precautions to take. Once it is known that a microbe is harmful, they can begin established protocols that allow them to determine the specific identity of the cell and determine an effective antibiotic against the microorganism.
Another benefit is the ability to quickly and directly diagnose which bacteria respond to which antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance can be a devastating problem in hospitals and other environments where individuals with already compromised bodies and immune systems may be exposed to and infected by increasingly high amounts of antibiotic resistant bacteria. Sometimes this results in a potentially fatal condition called bacterial sepsis, or septicemia. This is different from the viral sepsis that has been discussed in connection with COVID-19, though the scientists say their next steps will include investigating viral sepsis.
Treating sepsis is challenging. Giving the patient broad-spectrum antibiotics, which sounds like a good idea, might not help and could make the situation worse for the next patient. Letting bacteria come into close contact with antibiotics that do not kill them only makes them more resistant to that antibiotic and more difficult to fight the next time.
Culturing the patient’s tissues and homing in on the correct antibiotic to use can take time the patient does not have, usually eight to 10 hours. This new biodynamic process allows scientists to put the patient’s bacterial samples in an array of tiny petri dishes containing the tissue sentinels and treat each sample with a different antibiotic. Using Doppler, they can quickly notice which bacterial samples have dramatic metabolic changes. The samples that do are the ones that have reacted to the antibiotic — the bacteria are dying, being defeated and beaten back by antibiotics.
“When we treat with antibiotics, the bacteria don’t have to multiply much before they start to affect the tissue sentinels,” Dr. Nolte explained. “There are still too few bacteria to see or to measure directly, but they start to affect how the tissues behaves, which we can detect with Doppler.”
In less than half the time a traditional culture and diagnosis takes, doctors could tell which antibiotic to administer, bolstering the patient’s chances for recovery. The researchers worked closely with the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization to patent and license their technologies. They plan to further explore whether this method would work for tissue samples exposed to nonliving pathogenic cells or dried spores, and to test for and treat viral sepsis.
Click here to view a complete news release about the research.
