
A new treatment for strokes caused by bleeding in the brain that uses a magnetically controlled microrobot-enabled self-clearing catheter has been shown to be 86% effective in animal models, according to a paper published in Nature Communications. The research led by Dr. Hyowon “Hugh” Lee, associate professor of biomedical engineering in Purdue’s Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, involves collaboration with neurosurgeons in veterinary and human medicine.
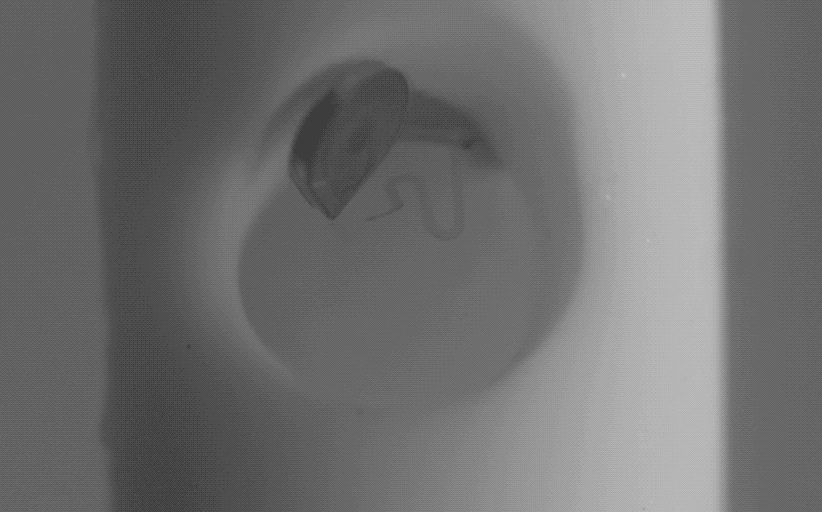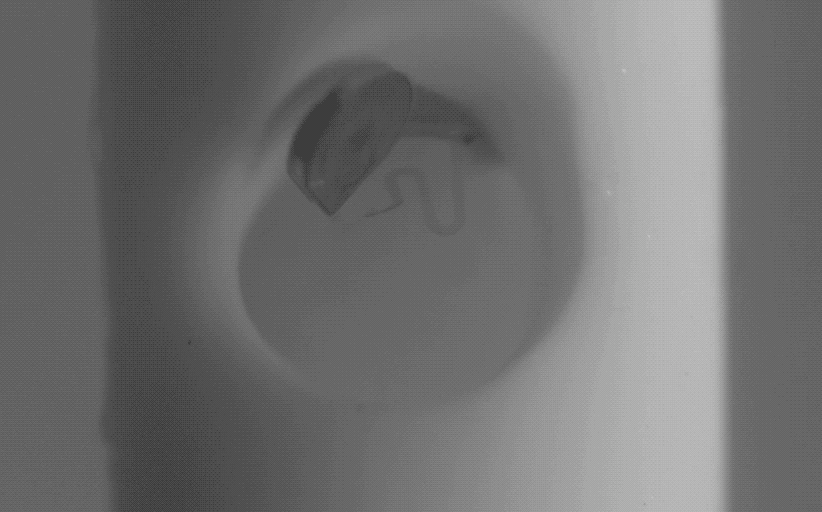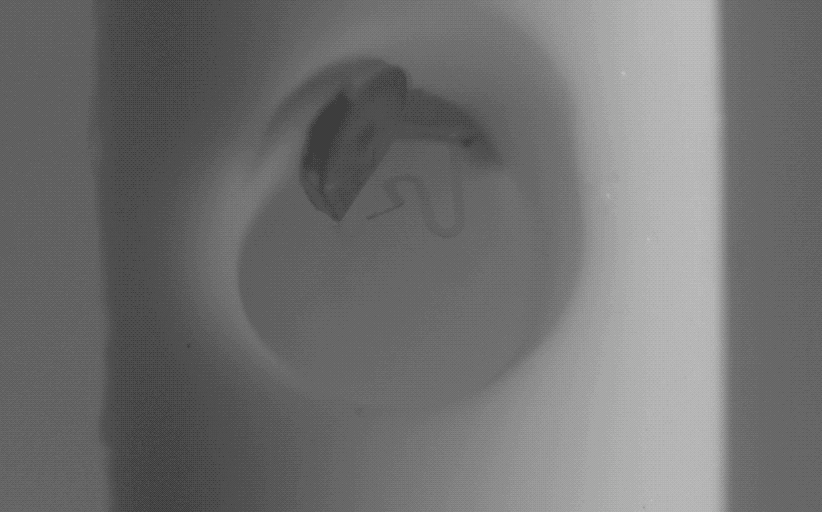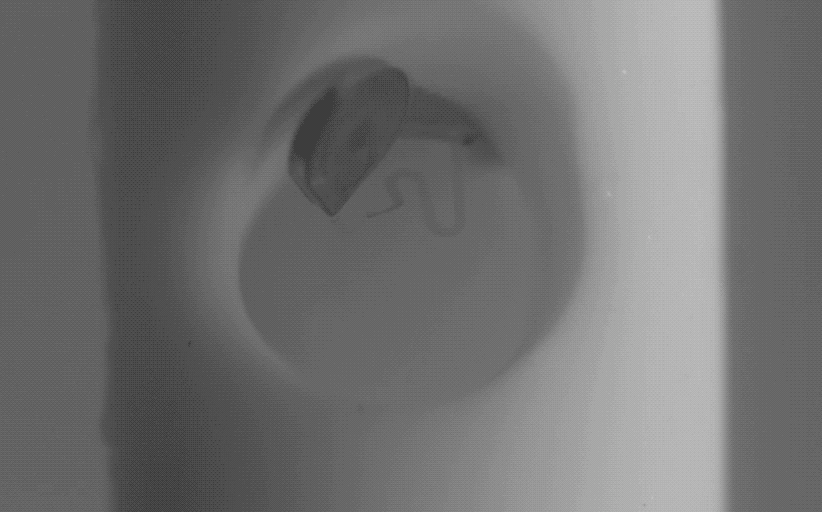
Dr. Lee created the magnetically controlled microdevice that removes blood accumulating in the brain during a stroke. The innovation was tested on porcine models of hemorrhage in collaboration with Dr. Timothy Bentley, associate professor of neurology and neurosurgery in the Purdue University College of Veterinary Medicine, and Dr. Albert Lee, from Goodman Campbell Brain and Spine in Carmel, Indiana.
The microrobots successfully removed the blood in six of the seven animals in the treatment animal model. “This innovation is a real advance in the care of strokes, which are notoriously difficult to treat,” Dr. Hugh Lee said.
The current gold standard to treat strokes is a blood thinner called tissue plasminogen activator, which cannot be used for some hemorrhagic strokes. “Patients with brain hemorrhages have a mortality rate of up to 50%,” Dr. Albert Lee said. “Currently there is no great therapeutic solution for intraventricular hemorrhage. The only other option is blood clot-dissolving drugs that have undesirable risks.”
Dr. Hugh Lee’s innovation, which was developed with a former graduate student, Dr. Qi Yang, can be remotely activated using externally applied magnetic fields. “There is no need for an implanted power source or complicated integrated circuit,” Dr. Hugh Lee said. “As you change the direction of the magnetic field, the microdevice moves like a compass needle with a magnet nearby. They can be part of an implantable shunt system or a part of extraventricular drainage systems.”
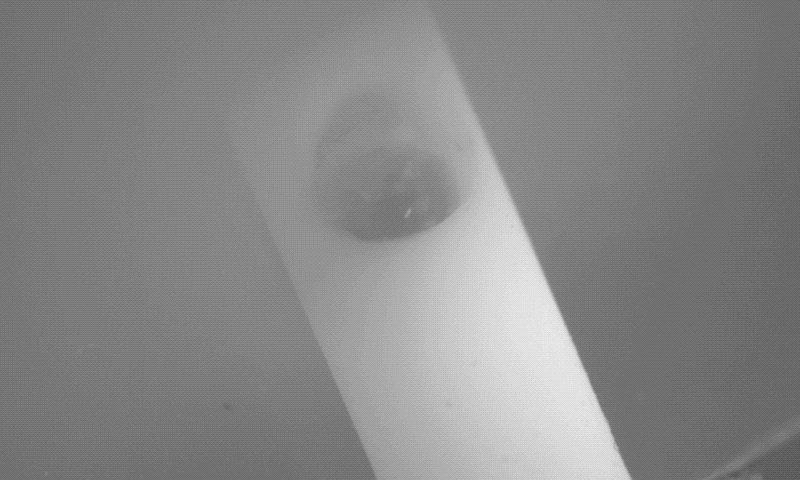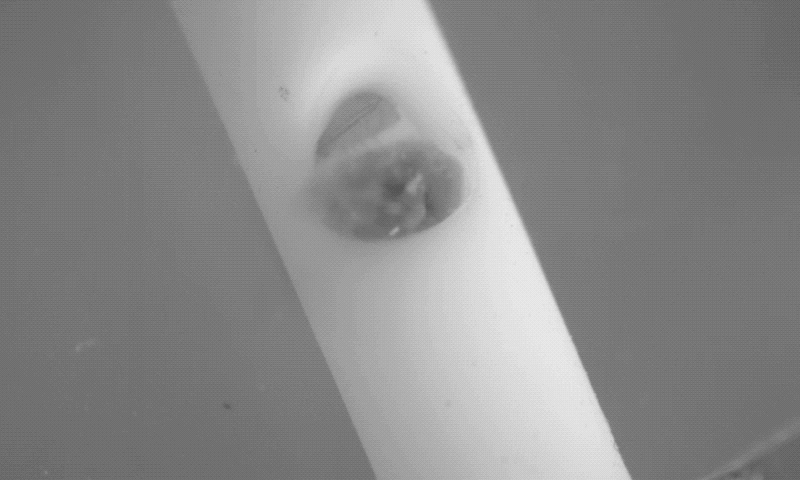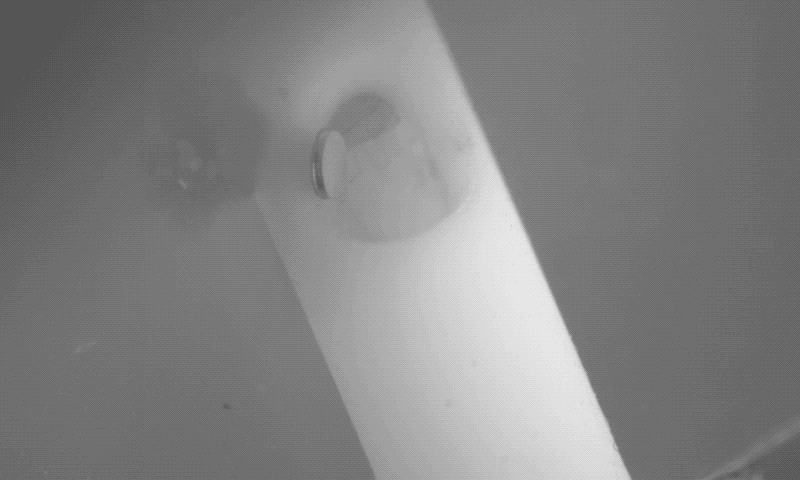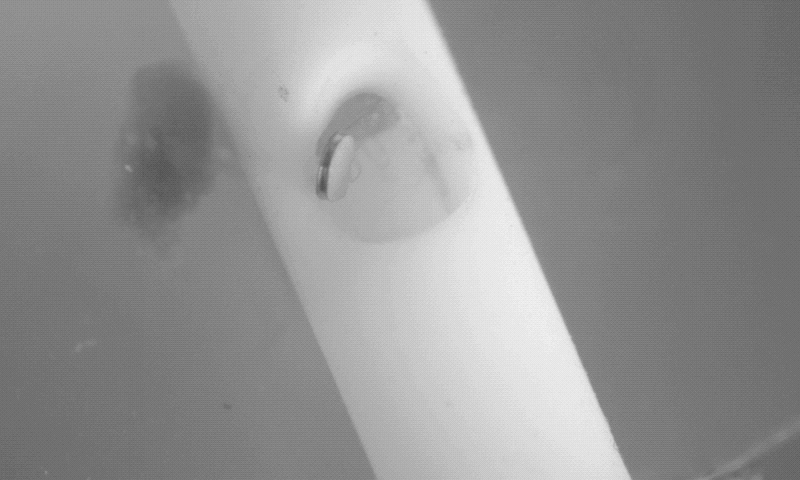
Dr. Hugh Lee disclosed the innovation to the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization, which has filed for a patent on the intellectual property. The next step to further develop the device is to receive approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for a first-in-human study.
Dr. Hugh Lee’s collaborative research was funded by grants from the Indiana Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute and the National Institutes of Health.
The Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization operates one of the most comprehensive technology transfer programs among leading research universities in the U.S. The office provides services that support the economic development initiatives of Purdue University and benefit the University’s academic activities through commercializing, licensing, and protecting Purdue intellectual property. In fiscal year 2021, the office reported 159 deals finalized with 236 technologies signed, 394 disclosures received, and 187 issued U.S. patents. The office is housed in the Convergence Center for Innovation and Collaboration in Purdue’s Discovery Park District, which is located adjacent to the main Purdue campus in West Lafayette.
Click here to view a complete news release from the Purdue Research Foundation.
