
Dr. Marxa Figueiredo, associate professor of Basic Medical Sciences in the College of Veterinary Medicine, played a leadership role on a team of Purdue University scientists who have created a new therapy option that may help halt tumor growth in certain cancers such as prostate, which is among the most common types of cancer in men. In 2018, approximately 324,000 men died from cancer in the United States. The combination of lung cancer, prostate cancer, and colorectal cancer equated to half of those deaths.
Large percentages of each of those cancers can be prevented or treated if caught early. “We have designed a therapy that can help recruit immune cells to kill cancer and also help repair bone and tissues damaged by tumors,” said Dr. Figueiredo, who is working with the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization to patent the innovation. “One of the best features of this technology is that it shows great promise in enabling treatment for many other cancers and diseases that could benefit from halting tumor growth and promoting bone repair.”
The therapy technology is presented in the journal Molecular Therapy: Methods & Clinical Development. The Purdue team used a protein called interleukin-27, or IL-27, which has shown promise in reducing tumor growth and helping stop cancer from spreading in the body. IL-27 is a cytokine, a kind of protein secreted by cells of the immune system that act as chemical messengers and can help the immune system target cancer and other diseases.
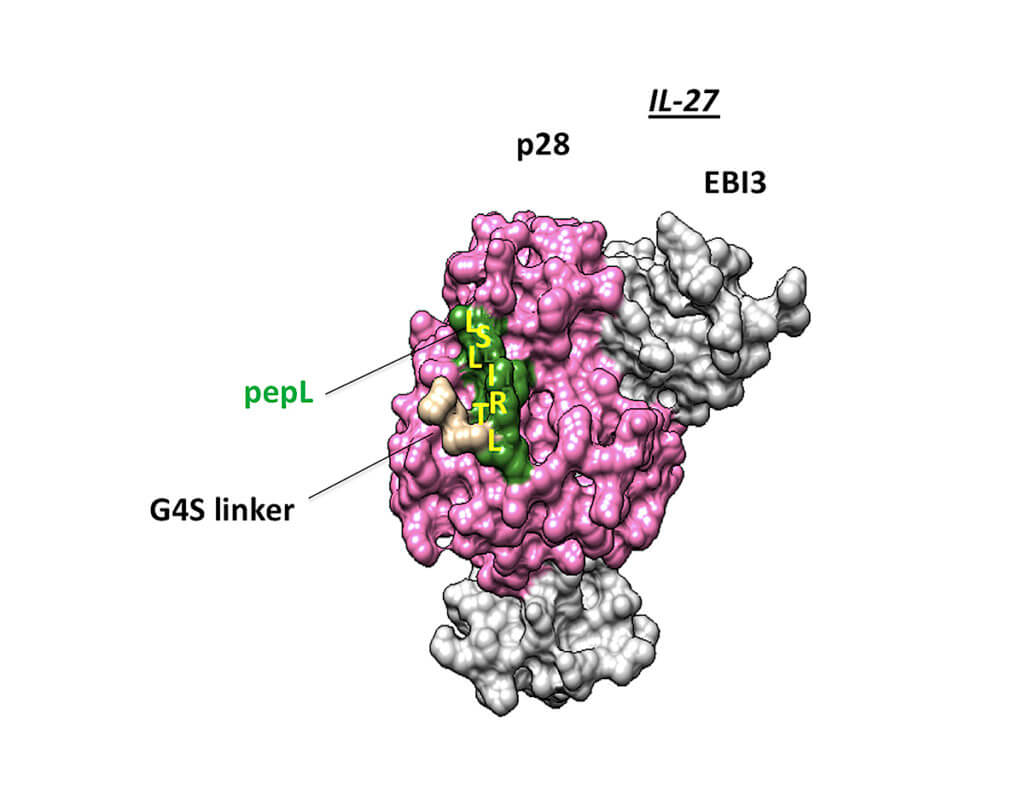
“Immune cells are naturally attracted to areas of the body with lots of signals that come from proteins such as IL-27,” Dr. Figueiredo said. “So, with our novel approach of targeting the IL-27 to the tumor or bone cells, we can use these proteins to produce signals that bring healthy cells to areas of the body with cancer or other disease and kill the tumors and begin the process of repairing bone and other musculoskeletal tissues.”
Dr. Figueiredo said the new Purdue therapy technology has applications for people and animals with many different types of cancer, including breast and lung, and other diseases where protein targeting could improve the immune system’s response.
The research team and the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization are looking for partners for this cancer therapy technology. For more information on licensing and other opportunities, contact Joseph Kasper of OTC at jrkasper@prf.org. Click here to view a complete news release about the research.
