Professor J. Paul Robinson in Purdue Veterinary Medicine’s Department of Basic Medical Sciences worked with a team of Purdue researchers to develop new technology to help stop the spread of foodborne illnesses, which kill 3,000 people a year. The technology combines innovative assays with laser pulses to detect these illnesses more efficiently.
The research team developed a lanthanide-based assay coupled with a laser that can be used to detect toxins and pathogenic E. coli in food samples, water and a variety of industrial materials. The two key features of the new technology are the incorporation of lanthanides and simple lateral flow paper-based assays.
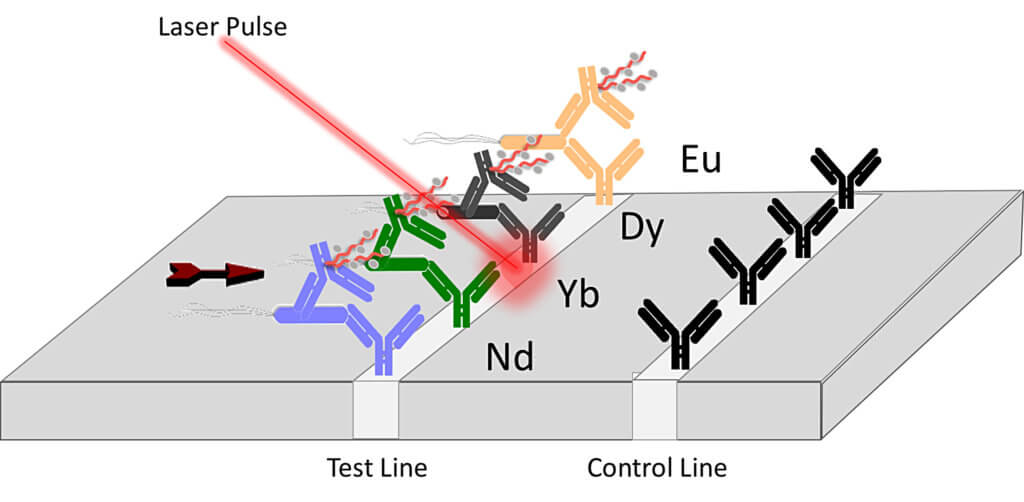
The Purdue team created a method for combining different heavy metals that, when linked to antibodies, can detect multiple agents in a single analysis. Their work is published in the January edition of Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.
“Our goal was to incorporate easily detectable elements into a paper-based assay which is low-cost and effective,” said Dr. Robinson, who holds a joint appointment as the SVM Professor of Cytomics in the College of Veterinary Medicine and professor of biomedical engineering in Purdue’s College of Engineering. “Designing a technology that is both low-cost but also accurate and can detect multiple antigens simultaneously was a critical factor in our decision to work on this problem.”
The innovators worked with the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization (OTC) to patent the technology in the United States and in Europe. “We are very excited about the acceptance of the intellectual property as this will enhance the possibility of finding commercial partners,” Dr. Robinson said. “The potential for moving this to handheld, field deployable use is something we see in the future.”
The approach uses a high-powered laser pulse to obliterate a sample, while simultaneously collecting the spectral signature of the resultant emission. These signals are then compared with a database that translates the signals into an identification of the toxin or pathogen.
The work published in the journal article shows the proof of principle and is the basis for significant expansion of the studies. The team is looking for partners. For more information, contact Dipak Narula of OTC at dnarula@prf.org and reference track code 2019-ROBI-68413.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service (ARS) and Center for Food Safety Engineering (CFSE) provided funding for the technology research in addition to Hatch Funds, which support agricultural research at land-grant institutions across the U.S.
Click here to view a complete news release.
