by Josh L. Clark, MS, RVT and Kelsey Wirt, MS, LVT
If you're passionate about animals and have an interest in science and medicine, then becoming a vet tech might be the perfect career for you. How do you become a vet tech? The journey to this rewarding profession typically involves several key steps, including education, credentialing, and gaining practical experience, all of which prepare you for the wide range of duties encompassed in vet tech jobs.
Your journey to becoming a vet tech can start as early as high school. Courses in biology, chemistry, and mathematics can provide a solid foundation for your future studies. Job-shadowing or working part-time at an animal shelter, veterinary clinic, or similar setting can give you valuable hands-on experience with animals.
The next step is to earn a post-secondary degree in veterinary technology. Most vet tech jobs require an Associate Degree and/or a Bachelor’s Degree in Veterinary Technology. Vet tech programs must be accredited by the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) in order for graduates to be eligible for credentialing. Coursework usually includes animal anatomy and physiology, veterinary pharmacology, animal nursing and nutrition, radiology, anesthesiology, and more.
After completing your degree, most states require vet techs to become credentialed (certified, licensed, or registered depending on the state). Although requirements can vary, this process generally involves passing the Veterinary Technician National Examination (VTNE), a standardized exam administered by the American Association of Veterinary State Boards. Some states also require passing a state exam in addition to the VTNE.
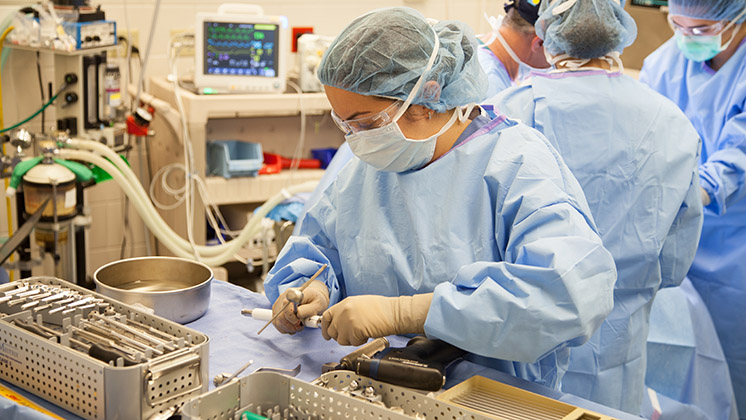
Gaining practical experience is a crucial step in becoming a vet tech. Many vet tech programs include internships or externships as part of their curriculum, allowing students to gain hands-on experience in a veterinary setting. After graduation, entry-level vet tech jobs can provide further practical experience.
Most states require vet techs to participate in continuing education (CE) to maintain their certification, licensure, or registration. The amount of CE required each year will vary from state to state. This helps vet techs stay up-to-date with the latest developments in veterinary medicine.
Becoming a vet tech involves a combination of academic preparation, credentialing, and hands-on experience. Being a vet tech offers the opportunity to improve the health and well-being of animals every day. This rewarding profession also offers a variety of career paths in addition to working in a clinical setting such as research, education, shelter medicine, practice management, and more.
Find your calling as a Purdue Veterinary Nurse!
Not quite ready to apply? Connect with us to learn more.

A concise guide examining the benefits and drawbacks of in-person veterinary technician education, including hands-on learning, networking, and challenges in flexibility and costs.
Read more
Explore scholarships, federal aid, and veterinary partnerships as invaluable resources to afford vet tech school tuition and overcome financial challenges in pursuing a veterinary technician career.
Read more
Explore the contrasting paths of becoming a veterinarian versus a veterinary technician, weighing factors like education, financial implications, and hands-on animal care. This comprehensive guide aids in discerning the best-fit veterinary career, backed by insights from Purdue's esteemed programs.
Read more